UPS Battery Sizing
Various techniques exist to enable the correct selection of batteries for UPS applications. The procedure described below is one of the more common. It is also possible to use the IEEE 485 method (see link at the bottom of the page).
Battery Types
Typically the following battery types are used in UPS systems:
- Lead Acid/Plante Battery
- Lead Acid/Antimony Battery
- Lead Acid/Calcium Battery
- Lead Acid/Calcium, Maintenance-free Liquid Electrolyte Battery
- Lead Acid/Calcium, Maintenance-free Gelled Electrolyte, Sealed Battery
- Lead Acid (Special Alloy), Suspended Electrolyte, Maintenance-free, Sealed Battery
- Nickel Cadmium, Pocket Plate Liquid Electrolyte Battery
Battery Sizing
Example of UPS battery sizing
Select the battery model number and quantity (using the typical watts per cell table) for a 300 kVA UPS, 94% efficiency, power factor of 0.8, for a backup time of 15 minutes.
The UPS battery bus voltage is 480 V. The typical table is for 12 V batteries (six cells of 2 V each).
Quantity of batteries per bank = 480/12 = 40 batteries
Number of cells per bank = 40 x 6 = 240 cells
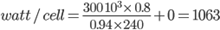
Looking at the capacity, we see that the required watt/cell is too much for one bank. However, various options are available, for example if we decided to use three banks in parallel:
watt/cell (three banks in parallel) = 1063/3 = 354
- select a S12V370(F) battery
Total number of batteries required
= 40 (per bank) x 3 (banks) = 120
Manufacturers provide sizing information for their batteries. Generally this information assumes a room temperature of 25oC. Batteries which will be operated at different temperatures continuously should be calculated specifically for that temperature.
Batteries are generally sized using [Watts] per cell or on [Ampere] per cell.
Watts per cell method
Normally information supplied for lead acid batteries designed for short discharge times (5-120 minutes) is in the form of kilowatts per cell tabulated for various back-up times. The required [Watts] per cell are given by:
![Image [4] Image [4]](http://myelectrical.com/Portals/0/SunBlogNuke/2/Windows-Live-Writer/UPS-Battery-Sizing_E56B/Image%20%5B4%5D_thumb_1.png)
Where:
VA = VA of the load
pf = power factor
η = efficiency of the UPS
N = Number of cells
Al = any addition load connected to the batteries (in VA)
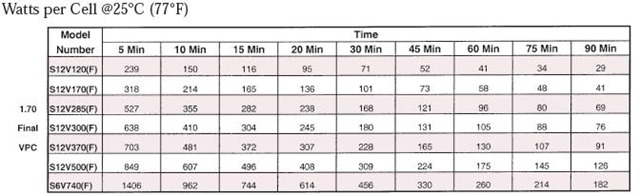 Typical Performance Specification (Amperes per Cell @25 °C)
Typical Performance Specification (Amperes per Cell @25 °C)
Amperes per cell
Average Battery Voltage
Battery voltage varies in use - staring high and then decreasing to it's end of discharge voltage. Taking into account this variation, makes calculation more complicated.
More often, an average voltage value is taken and calculations based on this.
If unsure about what the average value to use, then the end of discharge voltage could be used (as this is on the safe side).
Long term discharge lead acid batteries and most nickel cadmium batteries are sized using charts expressed in available amps for specified periods of time. The required [Amperes] per cell is:
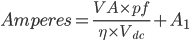
Where:
VA = VA of the load
pf = power factor
η = efficiency of the UPS inverter (dc to ac)
Vdc = Average Discharge Voltage
Al = any addition load connected to the batteries (in A)
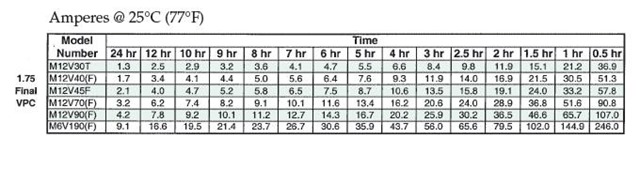 Typical Performance Specification (Amperes per Cell @25 °C)
Typical Performance Specification (Amperes per Cell @25 °C) Battery Charger Sizing
In general, a short term discharge battery can be recharged to 85% capacity in 8-10 times the discharge time. A long term discharge battery can be recharged to 85% capacity in a minimum of 8 hours provided the charger is sized properly.
Assuming the UPS is float charging, the following charging current Ic is required:
Where:
Ic = Charging current
IB = Battery current required
Td = Battery discharge (run) time
k = Safety factor (typically 1.5)
Tr = Battery recharge time
Ii = Inverter current required
Ia = Any additional load in (A)
See Also